The function you mean to call is rand not randomize. Please see C Reference - rand There are a few steps to using the rand function. First, you must seed the PRNG (see Wikipedia - Random Seed ). This is done using srand (see C Reference - srand ). Once the PRNG is seeded, you may start generating random numbers.
Dev C Download For Windows 7 If the expression is a non-void prvalue (after any lvalue-to-rvalue conversion that might have taken place), temporary materialization occurs. Compilers may issue warnings when an expression other than cast to void discards a value declared nodiscard. Tengo un problema, en el ejercicio que lo quiero meter, me dice que Error 'gotoxy' was no declared in this scope, entonces copie tal cual este ejercicio y me sale lo mismo, ya puse todas la librerias que son stdio, conio, windows, stdlib, math, entre otras, todas con.h al final y nada, ayudaaaaaa, mi version de dev c es 5.11. Responder Eliminar.
- Jul 21, 2014 If you intended to generate a random number,try using srand instead.Regarding randmax you will have to define it.
- Jan 16, 2015 There might be several things that could interfere with this code. Since this code actually does absolutely nothing the optimizer might get in your way and just do away with some things and also the “Spark” preprocessor sometimes gives you some headache.
- Source: vxl Source-Version: 1.17.0-2 We believe that the bug you reported is fixed in the latest version of vxl, which is due to be installed in the Debian FTP archive.
- Jan 30, 2011 gotoxy is a standard C function defined in, but it will not work in ANSI C compilers such as Dev-C. Because gotoxy is a Turbo-C specific function, which means it is not part of the standard. However, if you insist on using console functions, you can define your own function by using member.
- Dev C and C exit function. Why when I use it without include this header the the dev-c does not throw any error? 'exit' was not declared in this scope.
'Scope' is a concept which can be applied to many things in C++, and generally refers to the region of code in which something is accessible.
In the case of variables, variables are only accessible after they've been declared in the code. Variables which are defined in 'blocks', which generally means they're in some sort of structure, between curly brackets, are said to have the local scope as these are only accessible by things inside the block in which the variable was declared. Take for example the following in which the variable 'x' can only be accessed from the main function:
So far, we've learnt about many 'blocks', and as alluded to earlier, these can be classified generally by sections of code with curly brackets surrounding them - for example functions, while loops, for loops, if-statements, etc. Nested blocks (blocks inside blocks) also have access to the local variables of their parent blocks, take for example the following:
Note that for cases like the above where only one line should be treated as a 'block' for a statement, we can simply indent the single line and leave out the curly brackets - take, for example, the following:
In C++, we can actually create blocks without any special keywords like 'for' or 'if' just for general purpose by surrounding a section of code in curly brackets. Usually this isn't extremely useful, however in some cases it can provide a good way to isolate 'more local' variables:
On running the above example you can see that local variables (with the same name) are chosen over those of a wider scope. In the example the local variable is hiding the variable in the wider, 'main', scope, and as such there is no easy way of accessing the 'x' in 'main' from the block. This is why naming in this fashion should be avoided if possible.
If a variable (or anything else for that matter) is declared outside of any blocks, it is accessible from anywhere in the code. Variables declared this way are said to have global scope, however as convenient as these may be, they are often considered very bad practice. Take for example the following situation:
Once again the local variable takes preference over the global, and hence 5 is outputted. In this case, we could actually use the scope resolution operator (::) to target the variable using the global scope by simply not specifying anything on the left side of the operator:
Dev C Rand Was Not Declared In This Scope Video
Generally it's considered bad practice to give multiple variables the same name in situations where it's possible that scope could cause naming conflicts, and in cases like classes, some people like to use different notations to represent member variables to avoid naming conflicts. A popular naming convention is 'Hungarian Notation' which prefixes class member variables with 'm_', for example:
In the case of scope naming conflicts with classes, there is also a hidden pointer passed behind the scenes to every class member function (or at least those that aren't static, but we haven't learnt about that yet!). Take, for example, the above code snippet without the naming conventions:
Dev C++ Rand Was Not Declared In This Scope Meaning
Dev C++ Rand Was Not Declared In This Scope Video
It's clear what the programmer wants to do here, they want to set the member variables to the local scope parameters. The problem is that the 'age' and 'name' they're setting, are actually the parameters themselves! So if we added an 'output' member function and called this after constructing with the two parameters, we would see that the member variables still hold 'no value':

The best way to solve this would be to change the parameter/variable names. There is, however, another way we can accomplish this by using this hidden pointer. The hidden pointer is named this, and points to the object that the member function is being performed on. As such, we can dereference the pointer and use the dot operator to get the member variable of the object instead of the local member function one. As we covered previously, the (*a).b syntax is identical to the a->b syntax, and as such using the 'arrow' operator makes a lot of sense here. Although it's a bit messy, we could use the following:
C++ Rand Was Not Declared In This Scope

There are actually an awful lot of nice things that you can do with access to this hidden pointer. Presonus studio one 4.5 free download. A nice idea is making 'chain-able' member functions. So if related functions of a class return a reference to the object itself (the dereference of the 'this' pointer), then member functions could be chained up in a object.A().B().C() syntax! Note that if we don't set the return type of the function to a reference to the object type, a copy of the object will be passed each time, and so the chaining will completely break.
Dev C++ Rand Was Not Declared In This Scope History
Chaining member functions is pretty neat, although in this case there is a much cooler solution available if we overload some operators - but we haven't learnt about that yet.
Piano in Blue We were provided a unique opportunity to preserve an important piece of musical history in its final days. Word had come to us that the historic Clinton Recording Studios in midtown Manhattan was forever closing its doors, destined to be transformed into a modern condominium complex. Piano in blue vst crack full. Cinesamples – Piano in Blue v2 (KONTAKT) Piano in Blue is an exceptional instrument with great history, and we are thrilled to announce some updates that make this piano sound even better, along with some options that allow you greater control.”. Mar 26, 2020 There’s also a piano on the interface that allows you to see the notes that are being played. This plug is made by Bigcat Audio, the same makers for the Salamander plugin. I personally prefer the Salamander over this, however, this is another option to check out. The City Piano is a sampled Baldwin baby grand piano. Sep 22, 2015 Hello, here is a demo I've recently made with Piano in Blue: 'Le Piano Suspendu' (Full version feat. Piano In Blue) I really love the sound of this vst! I hope that you will like this second piano solo work.
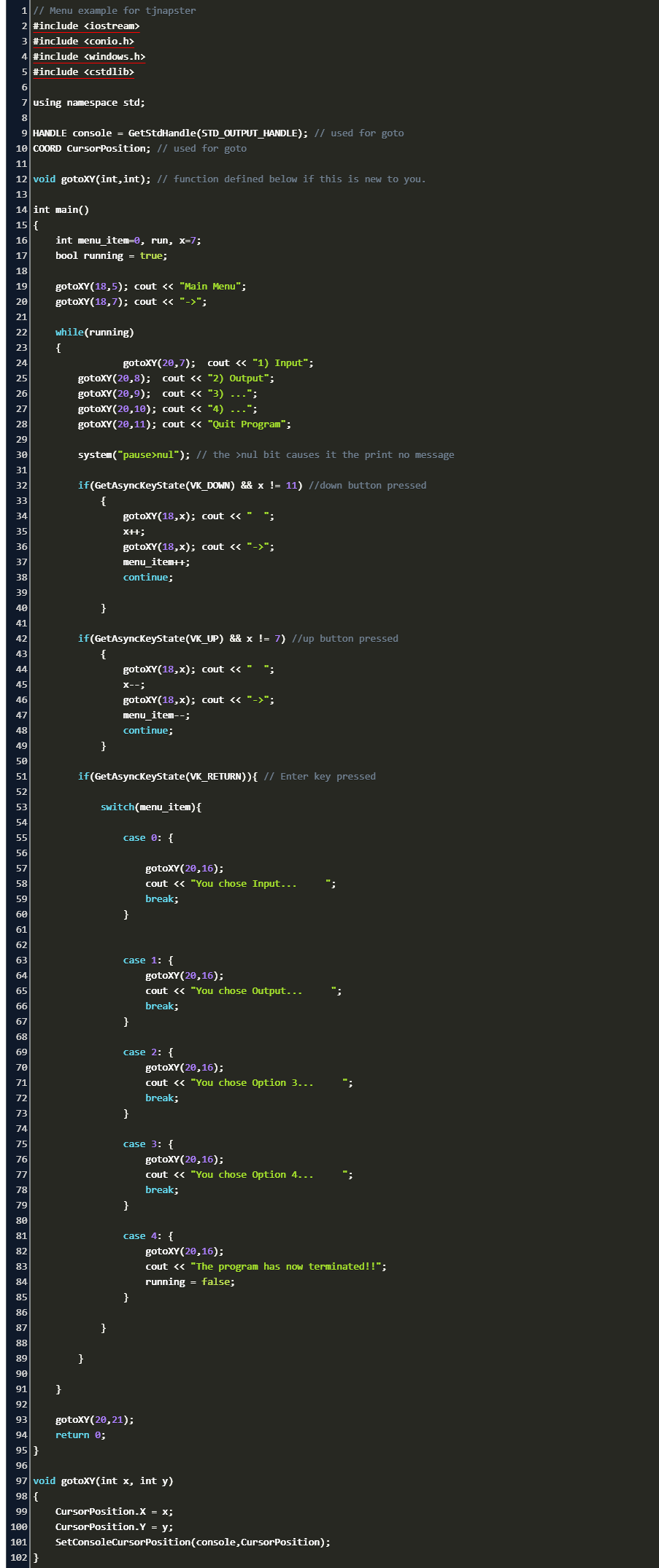
Using gotoxy() in Dev-C++
 January 30, 2011
January 30, 2011 gotoxy() is a standard C function defined in <conio.h>, but it will not work in ANSI C compilers such as Dev-C++. Why? Because gotoxy() is a Turbo-C++ specific function, which means it is not part of the standard. However, if you insist on using console functions, you can define your own function by using member functions available in <windows.h>
To use gotoxy() in Dev-C++, #include <windows.h> and insert this snippet before the main() function:
Gotoxy Was Not Declared In This Scope Dev C++
Gotoxy Was Not Declared In This Scope Dev Code
//Defines gotoxy() for ANSI C compilers.
void gotoxy(short x, short y) {
COORD pos = {x, y};
SetConsoleCursorPosition(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE), pos);
}